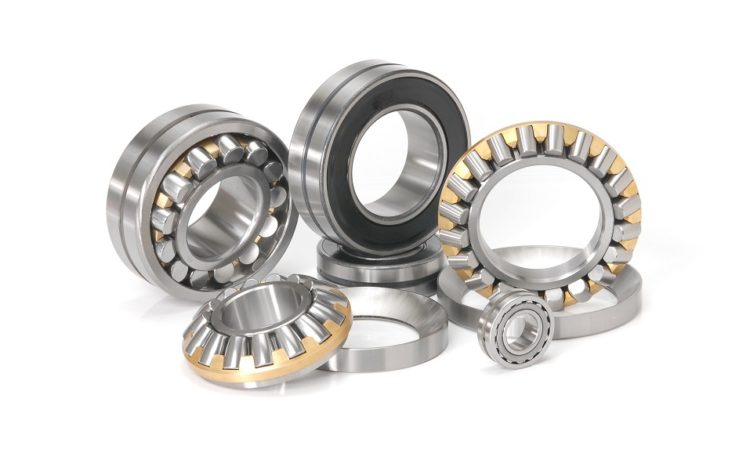
Ball bearings (INB) are a type of rolling-element bearings which enable movement by carrying weights, lowering friction, and positioning moving parts. Two distinct “races,” or bearing rings, reduce friction and surface contact across moving planes. The coefficient of friction is lower than on flat surfaces that rub against each other because of the spinning motion of the balls.
Design Of Ball Bearings
The four main components of a bearing (the ball separator) are the two rings/races and the two balls (the rolling elements). Both angular and radial contact ball bearings have inner and outer rings. Radial and angular ball bearings (INB) can support radial loads/weights perpendicularly to the axis.
While the housing is still, the outer race mounts to the housing. The outer race assists in the transfer of the radial loads from the bearing to the housing. The inner race mounts on a rotating shaft and supports and directs it while it rotates. The primary function of rolling components is to carry the weight and distribute it along raceways.
The inner race rotates slower than the rolling parts, but the rolling parts move faster. The separator acts as a barrier between the balls to prevent colliding. The divider is located between the balls.
Axial loads are also called thrust-bearing support loads. They run parallel to the axis. Two rings of the same diameter make thrust ball bearings.
What Are Ball Bearings Used For?
Ball bearings reduce rotational friction by supporting radial and axial loads. They can transmit the loads through balls, and at least two races are used to contain them. In many applications, a rotating assembly (such as a shaft or hub) is attached to one race while the other is stationary.
Due to the rotation of the bearing race, the balls spin in tandem with one another. Because of their rolling motion, the coefficient of friction for the balls is significantly lower than if they were in contact with two flat surfaces.
Their load capacity is usually lower than their size due to the smaller contact area between the races of the balls and the balls in ball bearings compared to other types of rolling element bearings. However, they can tolerate some discord between the outer and inner races.
Conclusion
Ball bearings, which are rolled components, help to move while decreasing friction in moving parts. Ball bearings can be made of various materials, such as steel, ceramics, and plastic.
Each material has its own unique characteristics, which makes them all different. Many ball bearings are available: steel-made, angular contact, deep groove, and wide other varieties. These types can be further subdivided into different groups, each with its own characteristics.