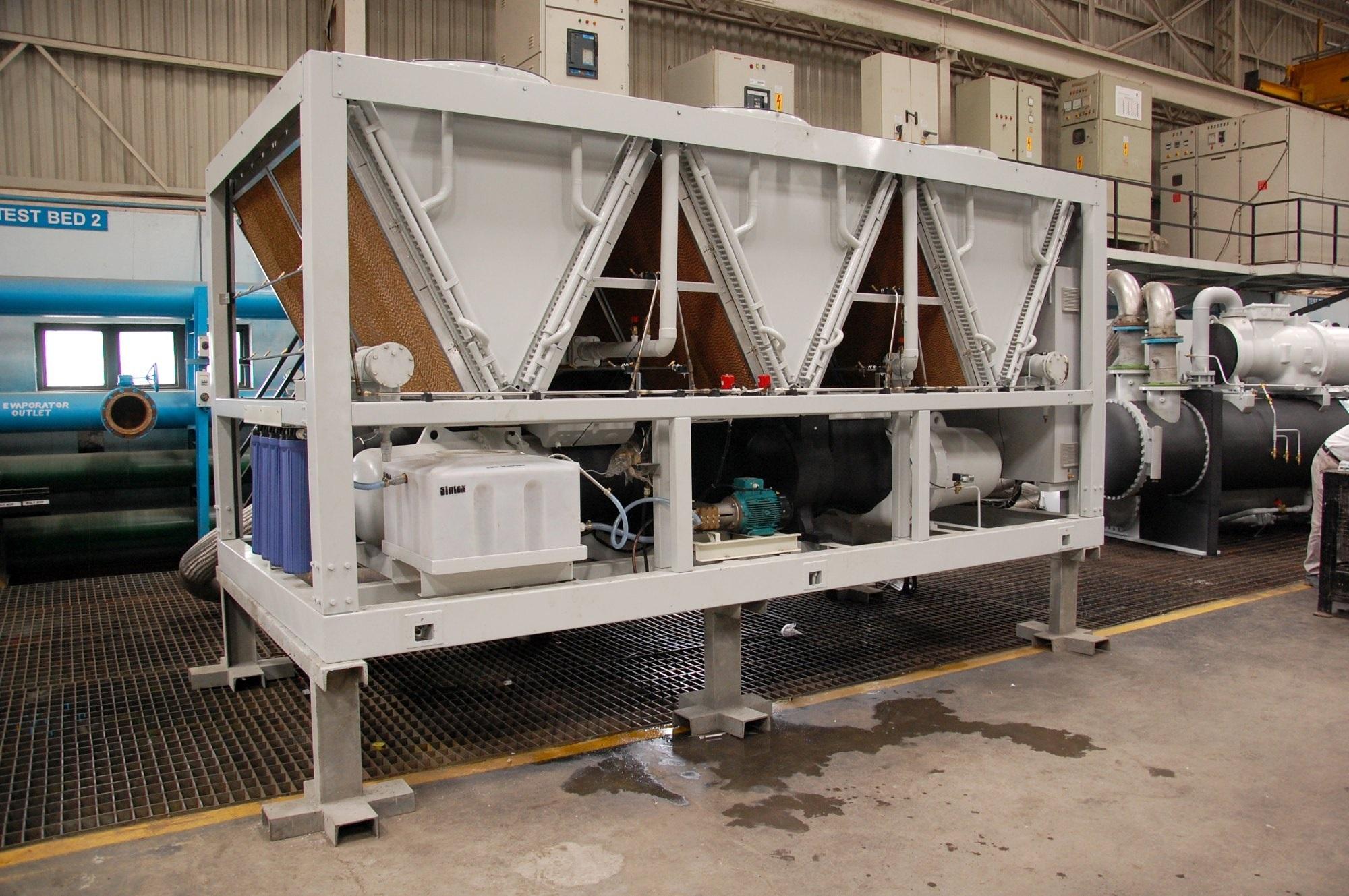
Adiabatic cooling is a method used in air-cooled chillers to reinforce their efficiency. Chillers are extensively used in industrial and commercial functions to take away warmth from processes or spaces. Traditionally, these chillers depend on mechanical refrigeration techniques that consume a big amount of power. Adiabatic cooling provides a extra sustainable and cost-effective different.
Understanding Adiabatic Cooling
Before delving into the effectivity facet, let’s first perceive what adiabatic cooling entails. Adiabatic cooling relies on the principle that when water evaporates, it absorbs heat from its surroundings, thereby reducing the temperature. By harnessing this natural phenomenon, adiabatic cooling methods can provide environment friendly cooling with out relying solely on mechanical refrigeration.
In air-cooled chillers, adiabatic cooling works by spraying a fantastic mist of water over the condenser coils. As the mist comes into contact with the new coils, it shortly evaporates, absorbing warmth from the encompassing air and lowering the coil temperature. This course of reduces the load on the mechanical refrigeration system, leading to energy financial savings.
Benefits of Adiabatic Cooling in Air-Cooled Chillers
The use of adiabatic cooling in air-cooled chillers provides several advantages:
- Increased Efficiency: Adiabatic cooling significantly improves the heat rejection capacity of air-cooled chillers. By pre-cooling the condenser coils, it reduces the workload on the refrigeration system, thereby enhancing its overall efficiency. This leads to lower energy consumption and operating costs.
- Enhanced Reliability: Adiabatic cooling helps maintain a steady operating temperature for the chiller, even in high ambient conditions. kaltra microchannel heat exchangers By mitigating the effects of ambient temperature fluctuations, it ensures consistent performance and protects the chiller from overheating.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Adiabatic cooling reduces the carbon footprint associated with air-cooled chillers. The decreased energy consumption translates into lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable operation.
- Flexibility: Adiabatic cooling systems can be retrofitted into existing air-cooled chillers, making them a versatile solution for improving efficiency. They can be easily integrated into various industrial and commercial applications without significant modifications to the chiller setup.
Considerations for Implementing Adiabatic Cooling
While adiabatic cooling offers numerous benefits, certain concerns ought to be taken under consideration throughout implementation:
- Water Usage: Adiabatic cooling techniques require a relentless supply of water to keep up their effectiveness. Proper water administration strategies should be put in place to ensure accountable utilization and decrease wastage.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to keep adiabatic cooling systems in optimal condition. This includes cleansing the nozzles, filters, and ensuring proper water therapy to prevent scale buildup or biological progress.
- Climate Conditions: The efficiency of adiabatic cooling varies depending on the climate and humidity ranges of the set up location. It is crucial to assess local weather patterns to discover out the potential advantages and limitations of implementing adiabatic cooling.
- Capital Investment: While adiabatic cooling can lead to long-term cost financial savings, the initial capital investment required for system installation should be thought-about. However, the return on investment can usually justify the upfront prices.
Conclusion
Adiabatic cooling provides a promising solution for increasing the efficiency of air-cooled chillers. By harnessing the ability of evaporation, this technique considerably reduces the workload on mechanical refrigeration systems, leading to vitality financial savings and enhanced performance. When carried out with careful consideration of factors similar to water usage and local weather conditions, adiabatic cooling can provide a sustainable and cost-effective various for cooling purposes.